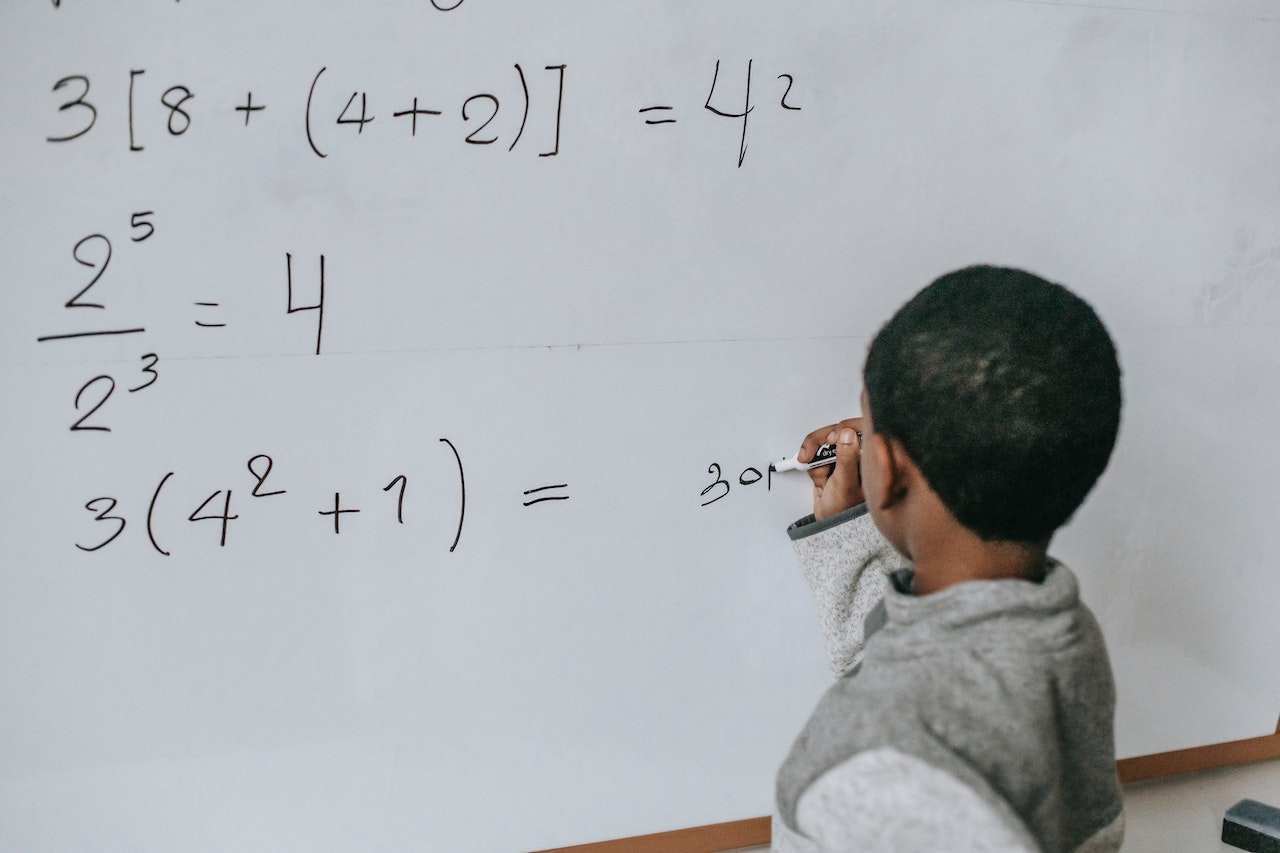Mathematics: The language of numbers and shapes
Published
Fundamentals of mathematics: from addition to geometry
The basics of mathematics form the foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts and applications. Mathematics is far more than just numbers and calculations; it is the language that describes the structure of our universe. This section introduces the essential concepts, starting with the most basic mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. These form the basis for any mathematical calculation. We will also look at algebra, an area that allows us to solve unknowns in equations and recognize patterns. Furthermore, we will enter the world of geometry, where we will study shapes, surfaces and volumes and understand how geometric principles are applied in the real world. These fundamentals lay the foundation for a deeper understanding of mathematics and enable us to master more complex mathematical challenges.
Mathematical concepts in reality: applications and meaning
Mathematical concepts permeate almost every aspect of our lives and are crucial to our understanding of the world and solving practical problems. In this section, we will explore how math is applied in the real world and why it plays such a fundamental role in science, technology, business, and many other fields. We will see how algebra is used to create complex financial models that allow businesses to make strategic decisions and how statistics is used to analyze data and draw sound conclusions. The importance of trigonometry is evident in architecture and the construction of bridges and buildings, while differential calculus is used in physics and engineering to describe motion and change. Mathematics is also crucial in medicine, where it forms the basis for the development of drugs and medical imaging. In short, mathematics is more than just an abstract discipline; it is a powerful tool that helps us understand and shape the world around us.
Mathematical puzzles and challenges: Brain teasers for the curious
Mathematical puzzles and challenges offer a fascinating way to train the brain and encourage logical thinking. They are not only suitable for math enthusiasts, but can also be extremely satisfying for anyone who enjoys puzzling and fiddling. One of the most well-known mathematical puzzles is Sudoku, where numbers have to be placed in a grid, following certain rules. This simple game can have surprisingly complex solutions and is a great tool for sharpening spatial thinking skills. The game of chess is another mathematical puzzle that has fascinated people for centuries. It requires strategic thinking and the ability to plan future moves. In addition, there are a plethora of math brain teasers that span areas such as logic, algebra and geometry. These challenges are not only entertaining but also educational and promote problem-solving skills. Although math is often perceived as abstract, math puzzles and challenges can turn it into a fun and tangible form that excites people of all ages.
The history of mathematics: from the ancient Greeks to modern times
The history of mathematics is a fascinating journey through the development of mathematical concepts and knowledge over the centuries. It ranges from ancient Greek scholars such as Pythagoras, who formulated the famous Pythagorean Theorem, to modern mathematicians such as Andrew Wiles, who proved Fermat's Last Theorem. In ancient times, the Greeks laid the foundations for many mathematical principles, including Euclid's geometry and Diophantus' arithmetic. During the Middle Ages, mathematical advances were made in the Islamic Empire, and in the Renaissance, mathematics experienced a rebirth with figures such as Leonardo da Vinci and Johannes Kepler.
The 17th and 18th centuries brought groundbreaking developments, including Newton's and Leibniz's calculus, which formed the basis for modern differential and integral calculus. In the 19th century, Carl Friedrich Gauss coined the theory of numbers and introduced the concept of non-Euclidean geometry. In the modern era, mathematicians such as Alan Turing contributed to the development of computer technology and laid the foundations for modern cryptography.
The history of mathematics is rich with discoveries and advances that have changed our understanding of the world around us. It shows how mathematics has played and continues to play a central role in different cultures and eras. Today, mathematical principles are indispensable in almost all areas of science and technology and form the foundation for many of our modern achievements.
The future of mathematics: new discoveries and technologies
Mathematics is in a continuous process of renewal and development. Today, we are experiencing an exciting era of mathematical research and innovation that is pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and advancing new technologies. One of the most exciting areas is quantum mathematics, which deals with the laws of quantum physics and has applications in encryption and the development of quantum computers.
Another promising area is topology, which is used not only in mathematics, but also in data analysis and neuroscience. The discovery and research of new prime numbers and the solution of previously unsolved mathematical problems are also of great importance.
Mathematical software and artificial intelligence are playing an increasingly important role in mathematical research. Machine learning and neural networks make it possible to create complex mathematical models and analyze large amounts of data, leading to new insights and applications.
The future of mathematics will also be shaped by collaboration between mathematicians and other scientists. Interdisciplinary research will allow mathematical concepts to be applied in new and exciting ways to address global challenges in areas such as climate change, health and energy efficiency.
Mathematics will continue to be a driving force for innovation and progress in our world. The coming years promise new discoveries, technologies and applications that will deepen our understanding of mathematics while strengthening our ability to solve complex problems.