Why is there a Labor Day?
Published
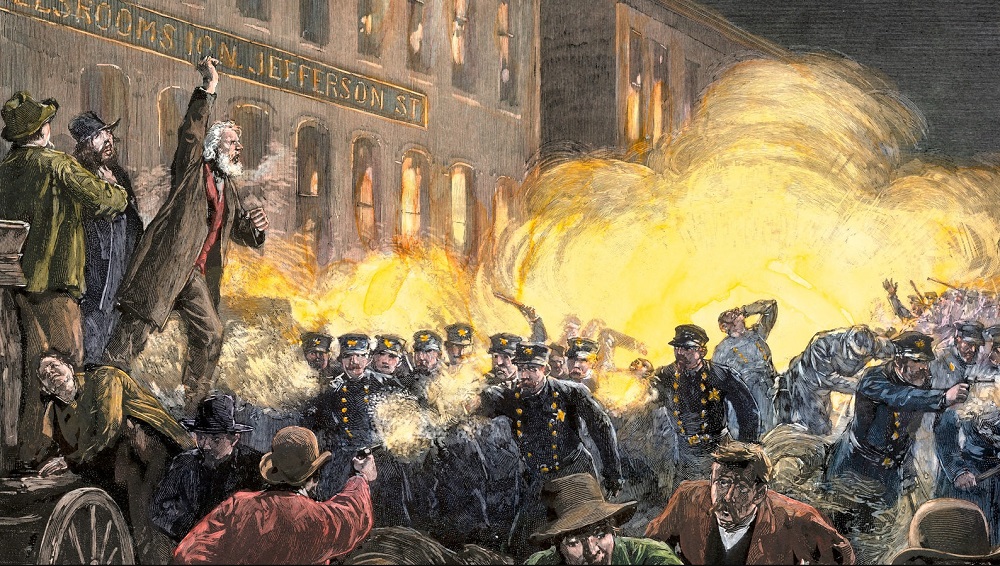
The Labor Day is an international holiday that is celebrated on 1 May and is recognized by law as a public holiday in many countries. It is often seen as a day of solidarity for the workers' movement and serves to recognize workers' rights and draw attention to their concerns.
Labor Day has historical roots in the labor movement and goes back to the workers' struggle for better working conditions, shorter working hours and fair wages in the 19th and early 20th centuries. May 1, 1886, in particular, played an important role when workers in the USA went on strike for the eight-hour day and there were violent clashes with the police.
| Date | Occasion | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| May 1 | Labor Day | - Public holiday to honor employees |
| - Recognition of the achievements of the labor movement | ||
| - Fight for better working conditions and rights | ||
| - Solidarity of the labor movement | ||
| - Focus on social justice and employee rights | ||
| - Rallies, demonstrations and events | ||
| - Collective bargaining and trade union demands |
Today, Labor Day is celebrated in many countries as a public holiday on which demonstrations, rallies and events take place. Trade unions, workers' organizations and other groups use this day to draw attention to current labour market issues, social justice and workers' rights.
Labour Day symbolizes the commitment to better working conditions, the protection of workers' rights and the recognition of their contributions to society. It is also an opportunity to emphasize the importance of solidarity and cooperation between workers.
Why is there a Labor Day?
Labour Day was introduced to recognize the rights and interests of workers and to draw attention to their concerns. The origins of Labor Day go back to the labor movement of the 19th and early 20th centuries, when workers worldwide fought for better working conditions and fair wages.
During the industrial revolution and the emerging capitalist economic system of the 19th century, working conditions were often extremely poor. Workers often worked long shifts, without adequate labor protection, underpaid and insecure jobs. Working hours were often excessively long, often 12 hours or more per day, and there was no regulation of working hours.
Over time, workers organized themselves into trade unions and other workers' organizations to stand up for their rights. The fight for an eight-hour day, better working conditions, decent pay and other social rights was a central concern of the labor movement.
May 1, 1886, played a particularly important role in the history of Labor Day. On this day, a nationwide strike for the eight-hour day began in the USA, involving workers from various industries and cities. The movement culminated in the Haymarket riots in Chicago, which led to violent clashes between workers and the police.
These events and the efforts of the labor movement ultimately led to the introduction of Labor Day as an international holiday. It is intended to honor the achievements of workers in terms of labor rights and social justice and to set an example of solidarity and unity of the labor movement.
Today, Labor Day is celebrated as a public holiday in many countries, with demonstrations, rallies and other events to draw attention to the current challenges and concerns of workers and to strengthen their rights.
Which countries do not celebrate Labor Day?
Most countries around the world celebrate Labor Day on May 1 or another date. However, there are some countries that do not have a specific holiday that corresponds to Labor Day. Here are some examples:
- United States: In the USA, Labor Day is not celebrated on May 1, but on the first Monday in September as so-called "Labor Day". It serves as a public holiday to recognize and appreciate the contribution of employees to society.
- Canada: Canada also celebrates Labor Day on the first Monday in September.
- Australia: In Australia, Labor Day, also known as "Labour Day", is celebrated on different days depending on the state. The dates vary between March and October.
- New Zealand: New Zealand also celebrates Labor Day on different days depending on the region. The dates vary between March and October.
- China: In China, there is no specific holiday that corresponds to Labor Day. However, May Day was long celebrated as the "Day of Struggle", which honors the working class and its achievements. However, this holiday was officially abolished in 2008.
It is important to note that even in countries where there is no specific Labour Day holiday, workers' concerns are still recognized and valued. In many countries, there are other holidays or national holidays that recognize workers and their rights.
Is Labor Day a public holiday?

Quelle: pexels.com
Labor Day, which is celebrated on May 1, is a public holiday in many countries. However, the exact legal recognition of Labor Day varies from country to country and can depend on national, regional or local level.
In many European countries, including Germany, France, Spain, Italy and most Scandinavian countries, 1 May is legally recognized as a public holiday. This means that employees are off work on this day and in some cases may also be entitled to additional public holiday pay or other benefits.
In addition, Labour Day is also recognized as a public holiday in many other countries around the world, including Argentina, Brazil, South Africa, Russia, India and many others. In some countries, such as the United States and Canada, Labor Day is celebrated on a different date, namely the first Monday in September.
It is important to note that the exact public holiday regulations vary from country to country. In some countries, May 1 may be considered a paid day off, while in others it may be considered a half holiday or a day with certain work restrictions. It is advisable to check the national laws and regulations of the country in question for precise information on the status of Labor Day as a public holiday.
How have trade unions contributed to the current state of the world of work?
Trade unions have contributed in many ways to the current state of the world of work. Through their representation of workers' interests and their fight for better Working conditions fair wages and social justice, trade unions have had a significant impact on the world of work and workers' rights. Here are some examples:
- Improved working conditions: Trade unions have played a decisive role in improving working conditions. They have campaigned for shorter working hours, regulated breaks, protection from Discrimination and harassment in the workplace, safe working environments and access to appropriate work equipment.
- Collective bargaining and wage formation: Trade unions negotiate collective agreements with employers on behalf of employees. This enables them to negotiate fair wages, benefits and working conditions that go beyond the statutory minimum standards. Collective agreements have influenced wage formation and contributed to the creation of fairer wage structures.
- Job security: Trade unions have worked to protect job security and minimize job losses. They have often negotiated with employers during company restructuring or redundancies to achieve fair dismissal procedures, severance pay or alternatives to dismissal.
- Social security: Unions have advocated for the introduction and maintenance of social benefits such as health insurance, pension plans and paid vacation. They have helped to improve social security for workers and promote financial stability.
- Equality and diversity: Trade unions have campaigned for equality for women, ethnic minorities and other disadvantaged groups in the workplace. They have campaigned against discrimination and for equal opportunities and pay for all workers.
- Right to collective bargaining: Unions have helped secure the right of workers to bargain collectively and organize. By strengthening the bargaining position of employees, trade unions have evened out the balance of power between employers and employees.
- Political influence: Unions have used political influence to influence laws and regulations that protect workers' rights. They have actively participated in policy discussions and advocated for labor law reforms and other measures to support workers.
It is important to note that the influence of trade unions can vary from country to country and region to region, depending on the strength and organization of trade unions as well as the political and economic situation. Nevertheless, trade unions have made a significant contribution to improving working conditions and labor rights at a global level.








